 Last month, the Court of Justice of the European Union issued a preliminary ruling on the right of natural persons to privacy with respect to the processing of personal data. In the case, Mr. Costeja González, a Spanish national, had lodged a complaint with the Agencia Española de Protección de Datos (AEPD), the Spanish Data Protection Agency, concerning a then 12-year-old announcement in La Vanguardia Ediciones SL, a Spanish newspaper, that mentioned a real-estate auction connected with attachment proceedings for the recovery of Mr. González’s social security debts. Mr. González wanted his personal data in the announcement removed from the La Vanguardia website. In addition, he wanted Google Inc. or Google Spain to remove the La Vanguardia web pages from its search results.
Last month, the Court of Justice of the European Union issued a preliminary ruling on the right of natural persons to privacy with respect to the processing of personal data. In the case, Mr. Costeja González, a Spanish national, had lodged a complaint with the Agencia Española de Protección de Datos (AEPD), the Spanish Data Protection Agency, concerning a then 12-year-old announcement in La Vanguardia Ediciones SL, a Spanish newspaper, that mentioned a real-estate auction connected with attachment proceedings for the recovery of Mr. González’s social security debts. Mr. González wanted his personal data in the announcement removed from the La Vanguardia website. In addition, he wanted Google Inc. or Google Spain to remove the La Vanguardia web pages from its search results.
The AEPD rejected the complaint against La Vanguardia because the Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs had ordered the announcement to promote the auction and secure as many bidders as possible. However, the AEPD upheld the complaint against Google Spain and Google Inc. The Google companies then brought separate actions before the Audiencia Nacional (National High Court), which stayed the proceedings and referred several questions regarding Directive 95/46 to the Court of Justice of the European Union.
In upholding the right of data subjects to have certain search results associated with their names removed from search engines, the Court of Justice stated that search engines may initially be able to process accurate personal data regarding a person. However, over time, this right may conflict with the Directive if such results are “inadequate, irrelevant or no longer relevant, or excessive in relation to those purposes and in the light of the time that has elapsed.” Accordingly, the right of privacy should be balanced against the economic interest of the search engine operator as well as the “interest of the general public in finding that information.”

 On November 30, Google was hit with yet
On November 30, Google was hit with yet  On Thursday, November 29, Google was named as the defendant in a
On Thursday, November 29, Google was named as the defendant in a  Massachusetts company Lexington Luminance LLC (“Lexington”)
Massachusetts company Lexington Luminance LLC (“Lexington”)  Yesterday, November 29, Brent Matthew Scott
Yesterday, November 29, Brent Matthew Scott  Yesterday, Google was named in a
Yesterday, Google was named in a  A federal court dismissed
A federal court dismissed 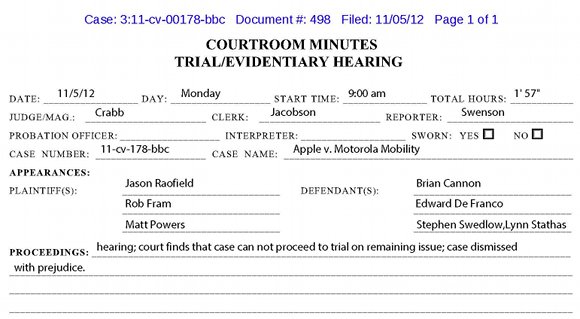
 After three years, language-learning software company
After three years, language-learning software company  On Monday, Apple filed an
On Monday, Apple filed an  According to a new infringement lawsuit filed Tuesday in federal court (read it below), the
According to a new infringement lawsuit filed Tuesday in federal court (read it below), the